Example Weighted/masked average
This example focuses on area weights (weighting by the area of the grid cell), but is generalizable.
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# or
# from imports import (plt, np, xr)
path = '~/shared-cmip6-for-ns1000k/historical/NorESM2-LM/r1i1p1f1/tas_Amon_NorESM2-LM_historical_r1i1p1f1_gn_200001-200912.nc'
tas_ds = xr.open_dataset(path)
path_area_weight ='~/shared-cmip6-for-ns1000k/historical/NorESM2-LM/r1i1p1f1/areacella_fx_NorESM2-LM_historical_r1i1p1f1_gn.nc'
areacella= xr.open_dataset(path_area_weight)
def masked_average(xa:xr.DataArray,
dim=None,
weights:xr.DataArray=None,
mask:xr.DataArray=None):
"""
This function will average
:param xa: dataArray
:param dim: dimension or list of dimensions. e.g. 'lat' or ['lat','lon','time']
:param weights: weights (as xarray)
:param mask: mask (as xarray), True where values to be masked.
:return: masked average xarray
"""
#lest make a copy of the xa
xa_copy:xr.DataArray = xa.copy()
if mask is not None:
xa_weighted_average = __weighted_average_with_mask(
dim, mask, weights, xa, xa_copy
)
elif weights is not None:
xa_weighted_average = __weighted_average(
dim, weights, xa, xa_copy
)
else:
xa_weighted_average = xa.mean(dim)
return xa_weighted_average
# %% [markdown]
def __weighted_average(dim, weights, xa, xa_copy):
'''helper function for masked_average'''
_, weights_all_dims = xr.broadcast(xa, weights) # broadcast to all dims
x_times_w = xa_copy * weights_all_dims
xw_sum = x_times_w.sum(dim)
x_tot = weights_all_dims.where(xa_copy.notnull()).sum(dim=dim)
xa_weighted_average = xw_sum / x_tot
return xa_weighted_average
def __weighted_average_with_mask(dim, mask, weights, xa, xa_copy):
'''helper function for masked_average'''
_, mask_all_dims = xr.broadcast(xa, mask) # broadcast to all dims
xa_copy = xa_copy.where(np.logical_not(mask))
if weights is not None:
_, weights_all_dims = xr.broadcast(xa, weights) # broadcast to all dims
weights_all_dims = weights_all_dims.where(~mask_all_dims)
x_times_w = xa_copy * weights_all_dims
xw_sum = x_times_w.sum(dim=dim)
x_tot = weights_all_dims.where(xa_copy.notnull()).sum(dim=dim)
xa_weighted_average = xw_sum / x_tot
else:
xa_weighted_average = xa_copy.mean(dim)
return xa_weighted_average
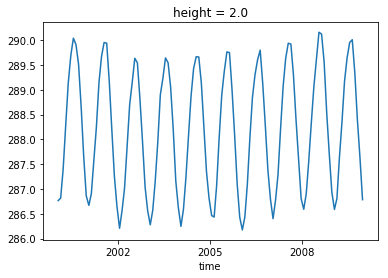
# ## Application 1: Weigted global average:
# Grid cells have different area, so when we do the global average, they have to be weigted by the area of each grid cell.
# Here we do it for 2 m temperature:
aw_xr = areacella['areacella']
glob_mean = masked_average(tas_ds['tas'], dim=['lat','lon'], weights=aw_xr)
glob_mean.plot()
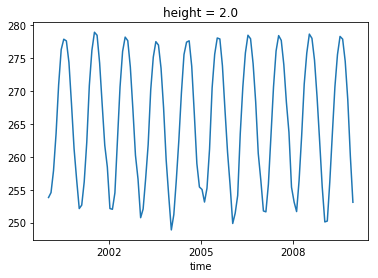
aw_xr = areacella['areacella']
# mask values with lat < 60 deg north
mask = tas_ds['lat']<60.
glob_mean = masked_average(tas_ds['tas'], dim=['lat','lon'], weights=aw_xr, mask=mask)
glob_mean.plot()