Setup model experiments
Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How to define a climate experiment?
How to run long experiments?
Objectives
Choose a scenario
Run a long experiment (14 months)
Analyze long experiment
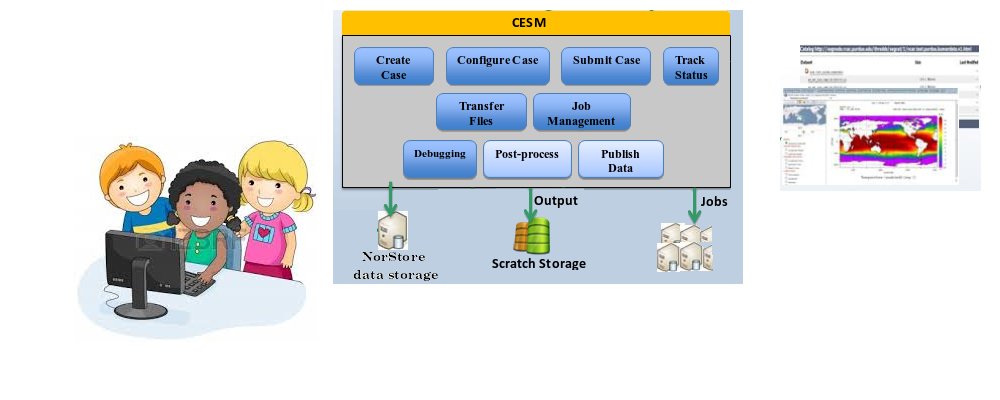
Introduce model experiments
Master students will work in pairs for this practical and to choose an experiment, adapt the namelist or make dataset changes following one of the predefined scenarios, then analyze the model outputs in pairs.
PhD students only
PhD students will get a more challenging exercise that will be defined later.
First choose your teammate: you will have to work together to set-up and run your experiment so make sure one of you has access to Saga.
Experiments
The goal is to run the experiment of your choice (to cherry pick from the list below) for a duration of 14 months, starting on 1st of January until 1st of March the following year. For this you will take the same restart file you already used for the test experiment of the previous practicals.
Each of the 4 experiments is given an explicit name:
- EXPNAME = CO2 Quadrupling of CO2 (change CO2 value to 1467 ppm > change the name list)
- EXPNAME = rockies Lowering of Rocky Mountains (set surface Geopotential to 0 from 30N to 50N and 235E to 260E > change the input data set)
- EXPNAME = sea_ice Melt of Arctic sea ice (set sea ice fraction to zero North of 40N > change the input data set)
- EXPNAME = SST Super El Nino (add +6 K to tropical Central and East Pacific SST from 5S to 5N, 180W to 85W > change the input data set)
- EXPNAME = himalaya Lowering of Himalaya Mountains and Tibetan Plateau (set surface Geopotential to 0 from 30N to 50N and 70E to 100E > change the input data set)
Make sure you define an environment variable EXPNAME, every time you login on Saga:
# define an environment variable for your experiment (CO2, rockies, sea_ice, SST or himalaya)
export EXPNAME=CO2
Here is the list of tasks to perform for the experiment of your choice:
- Create a new case for your experiment
- Setup experiment duration (1 month)
- Changing namelist or dataset
- Long experiment (14 months)
- Explain what you expect (not having performed any numerical simulation yet) the effect of the change you have picked to be on the general circulation in the atmosphere and send us your text by email.
Create a new case for your experiment
Use an appropriate name for your new experiment depending on what you selected (doubling CO2, sea_ice, etc.).
Suggested EXPNAME were given above.
To create a new case always involve executing the command create_newcase.
On Saga:# Adjust EXPNAME depending on your experiment (CO2, rockies, sea_ice, SST, himalaya)
export EXPNAME=CO2
module use /cluster/projects/nn1000k/modulefiles
module load cesm/2.1.0
#
# Simulation 2: Long simulation
#
create_newcase --case $HOME/cases/F2000climo-f19_g17.$EXPNAME --res f19_g17 --compset F2000climo --mach saga --run-unsupported --project nn1000k
Now you should have a new directory in $HOME/cases/F2000climo-f19_g17.$EXPNAME corresponding to your new case.
# Make sure EXPNAME is correctly defined!
cd $HOME/cases/F2000climo-f19_g17.$EXPNAME
As before we start a hybrid run from the control experiment.
On Saga:./xmlchange RUN_TYPE=hybrid
./xmlchange RUN_REFCASE=F2000climo.f19_g17.control
./xmlchange RUN_REFDATE=0010-01-01
We also need to define the START DATE for your experiment (that will make it easier to compare the outputs of the experiment with those of the same month from the control run).
On Saga:./xmlchange RUN_STARTDATE=0010-01-01
Setup your new experiment duration
Before running the long simulation (14 months), it is sensible to check your new settings on a short experiment that will take only a few minutes to run, to make sure everything is done as you expected (and if not, to correct any mistake).
You will run 1 month first, check the results and then restart the same experiment for several months.
Make sure you set the duration of your experiments properly.
On Saga:./xmlchange STOP_N=1
./xmlchange STOP_OPTION=nmonths
Now we are ready to set-up the model configuration and build the cesm executable.
On Saga:./case.setup
./case.build
The default history file from CAM is a monthly average but it is possible to change the output frequency with the namelist variable nhtfrq
- If nhtfrq = 0, the file will be a monthly average
- If nhtfrq > 0, frequency is input as number of timesteps
- If nhtfrq < 0, frequency is input as number of hours.
For instance to change the history file from monthly average to daily average, we set the namelist variable nhtfrq = -24.
We also need to copy restart files in your running directory, etc.
On Saga:# Make sure EXPNAME is set properly!
cd /cluster/work/users/$USER/cesm/F2000climo-f19_g17.$EXPNAME/run
wget https://zenodo.org/record/3721663/files/F2000climo.f19_g17.control.rest.0010-01-01-00000.tar.gz
tar zxvf F2000climo.f19_g17.control.rest.0010-01-01-00000.tar.gz
mv 0010-01-01-00000/* .
Now depending on your experiment case, you would have either to change the namelist or to change the input dataset.
Changing namelist or dataset
- Quadrupling CO2
- Lowering Rocky mountains
- Melt of Artic sea ice
- Super El Nino
- Lowering Himalaya mountains
Key Points
Evaluate various climate scenarii
Start an experiment from a control run
For PhD students: define, numerically implement and scientifically evaluate their own extreme geo-engineering solution to conteract doubling CO2