Search and Load CMIP6 Data via ESGF OPeNDAP
Search and Load CMIP6 Data via ESGF / OPeNDAP
This notebooks shows how to search and load data via Earth System Grid Federation infrastructure. This infrastructure works great and is the foundation of the CMIP6 distribution system.
The main technologies used here are the ESGF search API, used to figure out what data we want, and OPeNDAP, a remote data access protocol over HTTP.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import xarray as xr
xr.set_options(display_style='html')
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
#!/usr/bin/env python
from __future__ import print_function
import requests
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import numpy
# Author: Unknown
# I got the original version from a word document published by ESGF
# https://docs.google.com/document/d/1pxz1Kd3JHfFp8vR2JCVBfApbsHmbUQQstifhGNdc6U0/edit?usp=sharing
# API AT: https://github.com/ESGF/esgf.github.io/wiki/ESGF_Search_REST_API#results-pagination
def esgf_search(server="https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/esg-search/search",
files_type="OPENDAP", local_node=True, project="CMIP6",
verbose=False, format="application%2Fsolr%2Bjson",
use_csrf=False, **search):
client = requests.session()
payload = search
payload["project"] = project
payload["type"]= "File"
if local_node:
payload["distrib"] = "false"
if use_csrf:
client.get(server)
if 'csrftoken' in client.cookies:
# Django 1.6 and up
csrftoken = client.cookies['csrftoken']
else:
# older versions
csrftoken = client.cookies['csrf']
payload["csrfmiddlewaretoken"] = csrftoken
payload["format"] = format
offset = 0
numFound = 10000
all_files = []
files_type = files_type.upper()
while offset < numFound:
payload["offset"] = offset
url_keys = []
for k in payload:
url_keys += ["{}={}".format(k, payload[k])]
url = "{}/?{}".format(server, "&".join(url_keys))
print(url)
r = client.get(url)
r.raise_for_status()
resp = r.json()["response"]
numFound = int(resp["numFound"])
resp = resp["docs"]
offset += len(resp)
for d in resp:
if verbose:
for k in d:
print("{}: {}".format(k,d[k]))
url = d["url"]
for f in d["url"]:
sp = f.split("|")
if sp[-1] == files_type:
all_files.append(sp[0].split(".html")[0])
return sorted(all_files)
result = esgf_search(activity_id='CMIP', table_id='Amon', variable_id='tas', experiment_id='historical',
institution_id="NCAR", source_id="CESM2", member_id="r10i1p1f1")
result
# there are mulitple sources of the same data--need to pick one
files_to_open = result[-4:]
ds = xr.open_mfdataset(files_to_open, combine='by_coords')
ds
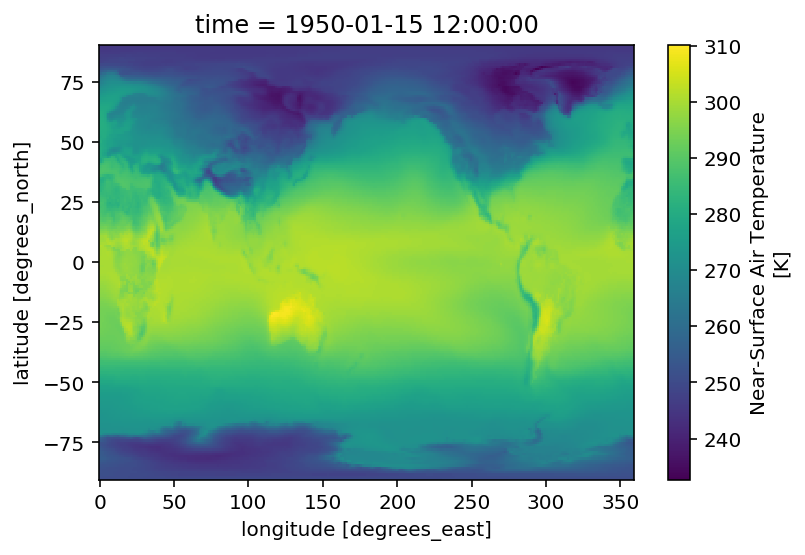
Plot a map from a specific date.
ds.tas.sel(time='1950-01').squeeze().plot()
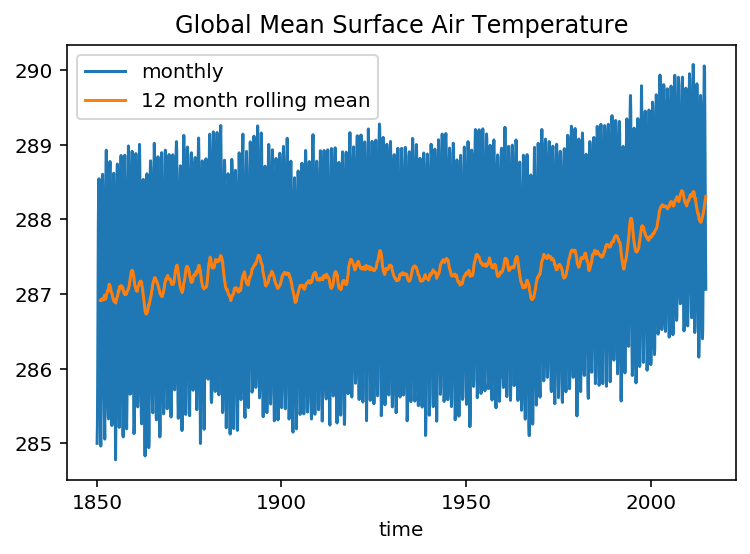
Create a timeseries of global-average surface air temperature. For this we need the area weighting factor for each gridpoint.
files_area = esgf_search(variable_id='areacella', activity_id='CMIP',
experiment_id='historical', institution_id="NCAR", source_id="CESM2")
ds_area = xr.open_dataset(files_area[0])
ds_area
total_area = ds_area.areacella.sum(dim=['lon', 'lat'])
ta_timeseries = (ds.tas * ds_area.areacella).sum(dim=['lon', 'lat']) / total_area
ta_timeseries
By default the data are loaded lazily, as Dask arrays. Here we trigger computation explicitly.
%time ta_timeseries.load()
ta_timeseries.plot(label='monthly')
ta_timeseries.rolling(time=12).mean().plot(label='12 month rolling mean')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Global Mean Surface Air Temperature')